Our 5 Key Takeaways from the Gartner Market Guide for Digital Commerce Payment Vendors
The Gartner® Market Guide for Digital Commerce Payment Vendors is a suitable resource to help you understand the complex and rapidly evolving market, as well as the related vendor landscape. It highlights key trends, the market direction, and attributes of the Representative Vendors, including TokenEx, which is recognized in the research*.
Here are our five key takeaways from the report that can help your business move toward treating payments as strategic.
1. The Digital Commerce Market is Massive and Still Growing
According to Gartner, “Global retail e-commerce grew at a rate of 16.8% year over year in 2021, to a total of $4.921 trillion, representing 19.6% of all retail sales worldwide.” The rise of B2B digital commerce is also notable, with businesses embracing consumer-like, omnichannel buying experiences. ‘’For many B2B buyers and sellers, this leverages traditional invoicing processes; however, more and more Gartner B2B clients are seeing demand for online, self-serve payment methods as well. In many cases, the ability to pay at the time of purchase attracts smaller merchants that may not qualify for traditional, credit-based invoicing.”
2. You Need to Consider Multiple Factors When Choosing a Payment Vendor
The Market Guide highlights that, “There are six key areas of focus and differentiation for vendors in the digital commerce payment market.” Businesses should consider these carefully when selecting a payment vendor.
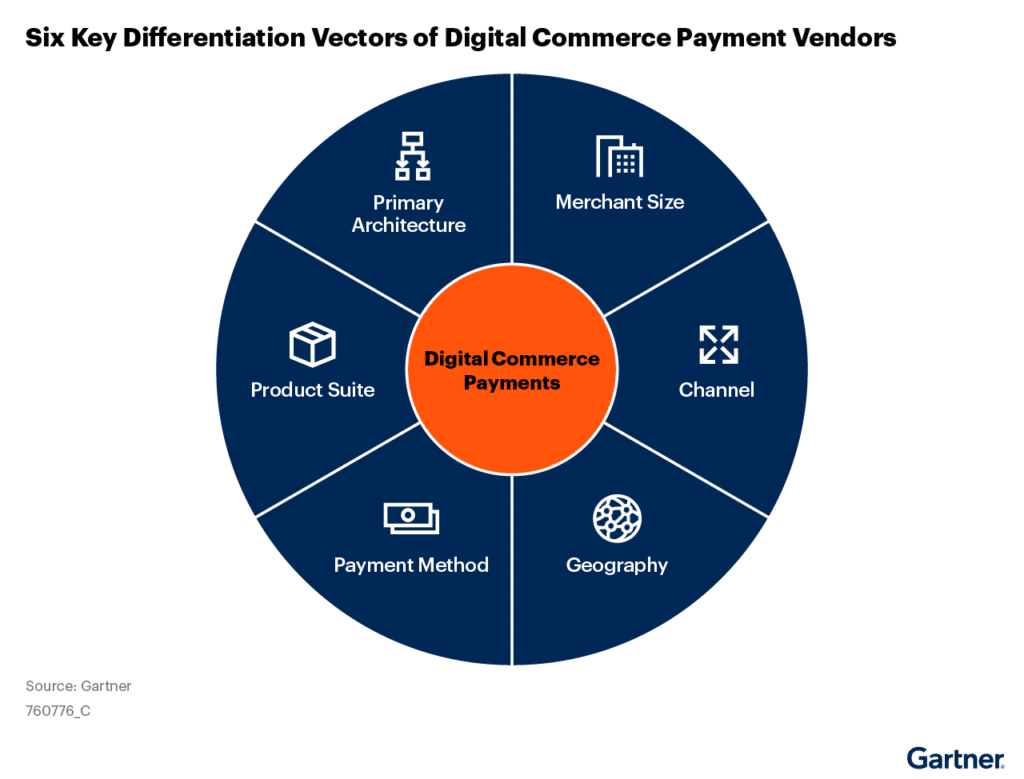
- Primary Architecture – Payment companies typically adopt one of three primary architectural models: full-stack, multiprocessor-agnostic, or multiprocessor merchant of record (MoR) or seller of record (SoR).
- Merchant Size – Most vendors have a customer distribution that is heavily weighted toward either the small and midsize business (SMB)/midmarket sector or larger midmarket and enterprise, often international, merchants. As the targeted merchant size and complexity increase, the sophistication of the offering is also growing.
- Channel – Some vendors have a more significant market share in the physical world — point of sale (POS), face-to-face and card-present transaction processing. Others have a bigger footprint in digital commerce, card-not-present processing.
- Geography – Although no one vendor yet offers every digital payment acceptance in every country, a handful of global vendors come close. Many vendors remain concentrated in a single region or country and have weaknesses in other locales.
- Payment Methods – Payment method support usually correlates with geographical coverage, as payment preferences are affected by culture, economy, regulatory, and other national or regional factors. All the providers included in this Market Guide offer at least major credit card acceptance services. Some may specialize in offering a broad range of alternative and local payment methods.
- Product Suite – Merchants may desire best-in-class, specialized point solutions or comprehensive one-stop-shop vendors that can address a wide breadth of payment ecosystem business needs. Ultimately, your decision should be driven by which criteria are most important to your business.
3. Integrations Across the Payment Ecosystem are Becoming More Essential
The report mentions that a significant factor in a merchant’s digital commerce payment vendor selection is the existence of productized integrations from the commerce, subscription, billing or other platforms of choice to the merchant’s preferred payment vendor. As aspects of the payment value chain become mature and even commoditized, vendors seek additional ways to maintain relevance and protect margins. They may look to achieve this by introducing adjacent technologies or services, such as:
- Fraud detection
- Electronic billing
- Subscription management
- Vertical solutions
- Issuing
- Payouts
According to Gartner, “A productized integration often relieves the merchant of much of the implementation and maintenance burden, but it may also limit flexibility and options for adding new features or supporting custom fields.”
Additionally, merchants will look to have a common payment strategy and architecture across all customer channels. Whether merchants opt for a full stack or a multiprocessor architecture, having a single payment gateway vendor across channels enables common tokenization strategies that connect in-store and online customer activity. This data linkage is important for popular buy online; pickup in store (BOPIS); or buy online, return in store (BORIS), and other multichannel purchase flows, as well as for creating a complete picture of an individual customer’s preferences and behaviors.
4. Alternate and Local Payment Methods Gain Adoption
The Market Guide states that “As credit cards’ share of digital commerce spend has dropped below 50% globally, alternative and local payment methods are critical to customer experience and sales conversion.”
Preferred payment methods vary dramatically by geography, driven by the unique cultural, technological, economic, and social behaviors of people in different countries and regions. Some non-card payments, such as direct debits and bank transfers, are familiar to businesses. However, the report mentions four alternative payment methods merchants should know.
- Digital Wallets: Consumers are redirected from the merchant’s website to digital wallet providers, where they authenticate their transactions securely by methods such as username and password, biometric device authentication, or an out-of-band one-time password. The consumer’s payment credentials, such as credit or debit card number, or bank account details, are stored securely by the digital wallet provider. In many cases, the consumer can also store a balance with the digital wallet provider and make payments from this stored balance.
- Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL): This is a special category of digital wallet that enables the consumer to receive goods while paying for them over time. It includes both deferred and installment options, although they are most widely known for installments.
- Offline Payments: Sometimes referred to as quasi-cash, these payment transactions are initiated through an online interaction with a merchant, but paid by the consumer at a later time in a separate transaction that is often face to face.
- Digital and Cryptocurrencies: This category includes cryptocurrencies and stablecoins, which are digital currencies built into a blockchain ledger. It also encompasses central bank-issued digital currencies (CBDCs), which are digital forms of central bank money that represent a claim on central bank cash accounts. As these payment methods continue to evolve, businesses must adapt to meet consumer preferences and regional demands for a seamless payment experience.
5. Use Payments as a Strategic Advantage
A key recommendation from Gartner is that application leaders responsible for digital commerce payment technologies should, “Treat payments as strategic, not operational.” Managing the payment experience as a source of differentiation offers the potential to boost profitability.
Another recommendation is that merchants should refine their global payment strategy by identifying the markets in which their organization does most business and its most commonly accepted or desired payment methods and services. Merchants should align vendor selection to the ability to support these markets, methods and services, for the current state and the foreseeable future.
Finally, effectively managing fraud detection processes to reduce losses without deterring good customers is crucial. Reducing losses while preserving a seamless experience for legitimate customers is essential to protect the bottom line.
Reduce overhead and costs by outsourcing payment services and consolidating payment vendors, where possible. Payment leaders should prioritize other recommendations to optimize digital commerce payment systems.
Learn More
Access a complimentary copy of the 2022 Gartner Market Guide for Digital Commerce Payment Vendors here to learn more about these trends and gain access to detailed company profiles for 19 payment vendors.
Attribution
Gartner, Market Guide for Digital Commerce Payment Vendors, Dayna Radbill, Akif Khan, 2 December 2022.
GARTNER is a registered trademark and service mark of Gartner, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and internationally and is used herein with permission. All rights reserved.
* Gartner does not endorse any vendor, product or service depicted in its research publications, and does not advise technology users to select only those vendors with the highest ratings or other designation. Gartner research publications consist of the opinions of Gartner’s research organization and should not be construed as statements of fact. Gartner disclaims all warranties, expressed or implied, with respect to this research, including any warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.