A 2021 Statista report indicates that an estimated 188 billion purchase transactions were made globally using Visa payment cards in 2020. This does not even include other credit card companies. Whether you have a traditional brick-and-mortar store or an online store, it’s imperative to understand how credit card processing works. Indeed, this is especially true since debit and credit cards are the most common forms of payment used by today’s customers. Keep reading to find out what is credit card processing, how it works, and why it is important for your business.
What Is a Credit Card Processor?
Credit card processing refers to a multi-step process necessary to successfully complete payments made with a credit card. In today’s digital age, transactions can take place just about anywhere – in person, online, over the phone, or by mail. Credit card processing involves numerous entities. This includes the consumer, merchant, payment gateway, credit card processor, card network, issuing bank, and acquiring bank.
Who Are the Key Players in Credit Card Processing?
- Customer – the person making a purchase.
- Merchant – the person or organization selling a product or service to the customer making a purchase.
- Payment gateway – this refers to the technology that connects a merchant to a payment processor. This process involves integrating with card-present (i.e., in-store purchases) and card-not-present (i.e., online purchases) payment environments, obtaining the payment information of customers’ transactions, sending these details to a payment processor or merchant bank, and then sending an “approved” or “declined” message to the merchant.
- Credit card processor – (or payment processor) this is the organization that helps the merchant, credit card network, and the cardholder’s bank communicates. Credit card processors and merchants must comply with the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
- Card network – (also called credit card network or credit card brand) this is the customers’ credit card brand, such as Discover, Mastercard, or Visa. These networks must set assessment and interchange fees.
- Issuing bank – (also known as the cardholder’s bank or consumer bank) this refers to the bank providing customers with their credit card. The issuing bank will determine whether the cardholder’s account has the funds to fulfill a transaction. If the account meets these requirements, the issuing bank will release those funds for settlement.
- Acquiring bank – (or merchant bank) this is the merchant’s bank, which is used for storing its business funds and receiving money from transactions. This type of bank can provide card readers and equipment to merchants, thus allowing merchants to accept card payments. Acquiring banks can also serve as credit card processors.
Now that we have discussed what a credit card processor is, let’s discuss how credit card processing works to securely process payments. This is crucial for ensuring customers can quickly and easily checkout.
How Does Credit Card Processing Work?
There are three primary steps involved in credit card processing, which include authorization, authentication, and settlement.
Authorization
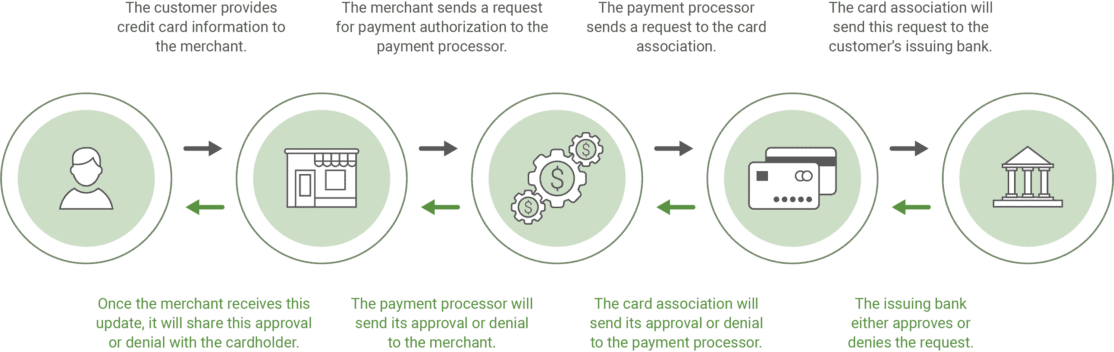
This is the initial step of the transaction process.
- The customer provides credit card information to the merchant, whether it’s at a store, online, or over the phone. This may involve entering the information on a website, swiping it at a POS or point-of-sale terminal, or providing the details over the phone.
- Then, the merchant sends a request for payment authorization to the payment processor.
- The payment processor sends a request to the card association.
- The card association will send this request to the customer’s issuing bank.
- The issuing bank either approves or denies the request and will send a message to the card association about this approval. This message will include the customer’s credit card number, expiration date, billing address, security code, and transaction amount. If the cardholder doesn’t have enough funds or credit to make a purchase, this will likely lead to a card being declined. Suspicious card activity may be flagged and thus denied for security measures.
- After receiving this request, the card association will send its approval or denial to the payment processor.
- The payment processor will send its approval or denial to the merchant.
- Once the merchant receives this update, it will share this approval or denial with the cardholder.
- If the transaction request is approved, the merchant will then provide the item or service. However, denied requests mean that the customer would have to use an alternative payment method to receive the product or service.
Authentication
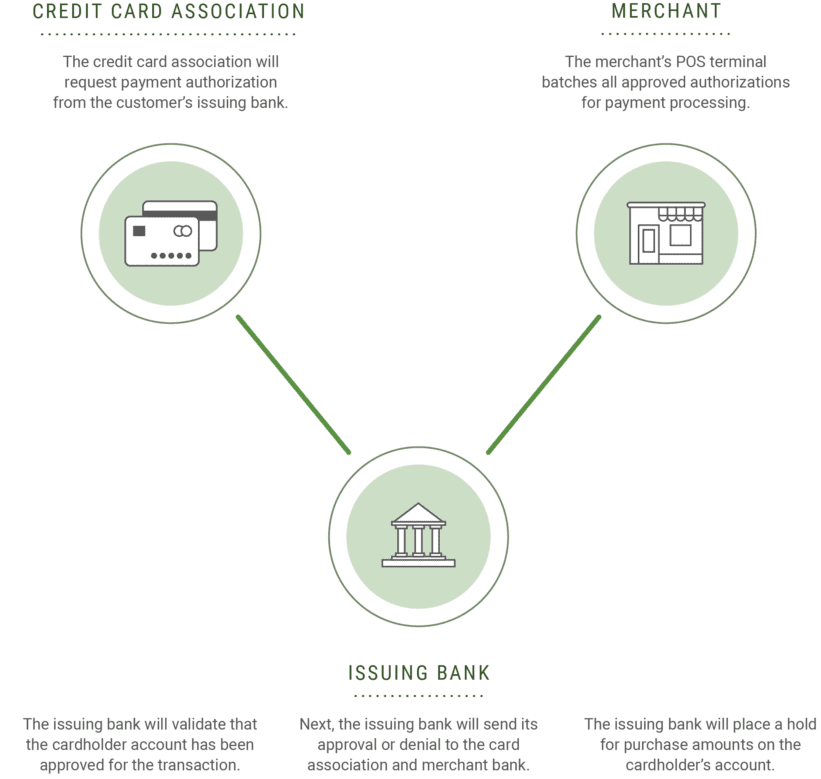
This is the second step, which occurs after the physical transaction has been made. The issuing bank must ensure that the transaction is valid.
- The credit card association will request payment authorization from the customer’s issuing bank.
- The issuing bank will validate that the cardholder account has been approved for the transaction and then check the identifying information.
- Next, the issuing bank will send its approval or denial to the card association and merchant bank.
- The issuing bank will place a hold for purchase amounts on the cardholder’s account (i.e., it will show up as pending on the customer’s account).
- By the end of that business day, the merchant’s POS terminal batches all approved authorizations for payment processing.
- The merchant will send the customer a receipt as proof of the purchase.
Settlement
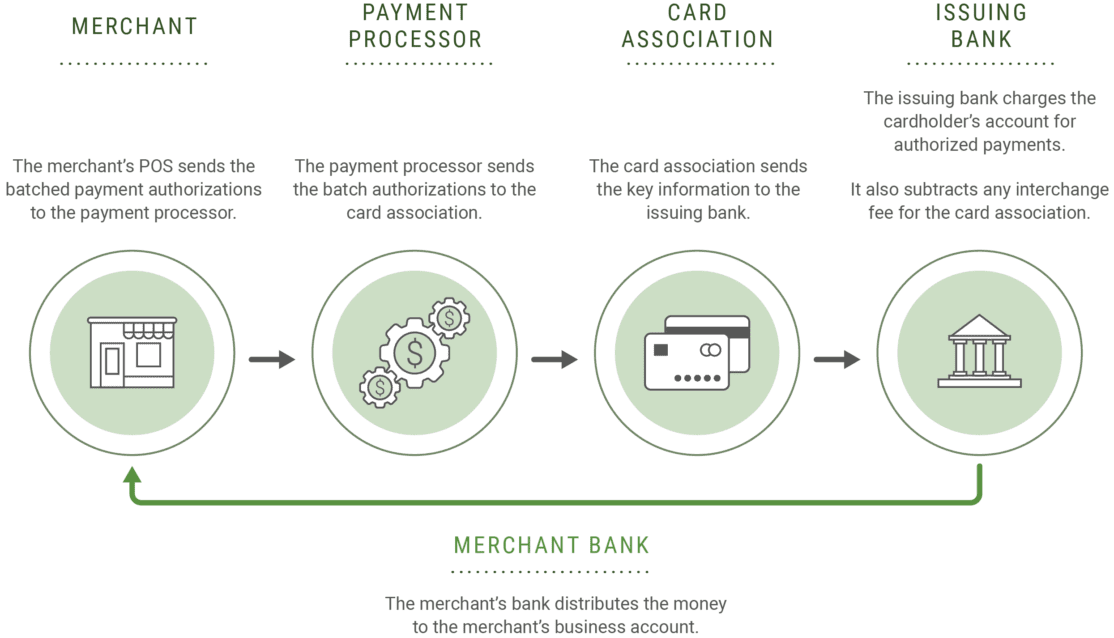
This is the final step of credit card processing, in which the merchant receives the funds from the customer’s bank. Keep in mind that the settlement phase can take several days depending on the specific card network being used.
- The merchant’s POS sends the batched payment authorizations to the payment processor.
- The payment processor sends the batch authorizations to the card association.
- Then, the card association sends the key information to the issuing bank.
- The issuing bank charges the cardholder’s account for authorized payments.
- The issuing bank also subtracts any interchange fees for the card association and then transfers the remaining funds to the merchant’s bank.
- Once received, the merchant’s bank distributes the money to the merchant’s business account.
- Finally, the issuing bank updates the customer’s account statement to reflect the recent transaction.
Why Is Credit Card Processing Important for Your Business?
As a business owner, it may feel like this was an overload of technical information. However, if you accept credit and debit card payments, it is essential to have a basic understanding of what credit card processing is and how it works. Indeed, this can help you optimize your payment processing to save you time and money, as well as boost efficiency at your business. It’s helpful to understand each step and who is involved. In turn, you will have a better grasp of the different aspects of the process and how this affects your business and customers.
Furthermore, credit card processing is a necessary part of processing card payments in a secure, timely manner for customers. By working with a credit card processing company, you can provide a positive checkout experience for your customers. When customers feel confident that your business is trustworthy and safe, they will be more likely to make repeat purchases and stay loyal to your brand.
Final Points
When choosing a payment processor, a key feature to check for is security protection regarding handling transactions. The processor company should meet PCI and EMV compliance requirements, as well as require additional card information from cardholders. In turn, this can help mitigate credit card fraud, as cybercriminals are less likely to have all the details of a customer’s card. Additionally, the processor should offer the leading security technologies for businesses, such as multi-factor authentication, encryption, and tokenization. If you are interested in learning more about how to protect your most sensitive data, contact TokenEx today. Our company is dedicated to helping you meet your business needs and giving you peace of mind that your customer’s payment information is protected via our tokenization solution.
How to Choose
a Tokenization Solution
Make sure you’re asking the right questions by reading this resource.